Introduction (100 words):
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Immunoglobulin A (IgA) – the unsung hero of our immune system responsible for safeguarding our mucous membranes. In this blog, we will delve into the world of IgA, exploring its crucial role in immunity, its production, and its significance in maintaining our overall health. Join us as we unravel the hidden potential and wonders behind this remarkable antibody.
Keywords: Immunoglobulin A, IgA, mucosal immunity
Section 1: Understanding Immunoglobulin A (200 words)
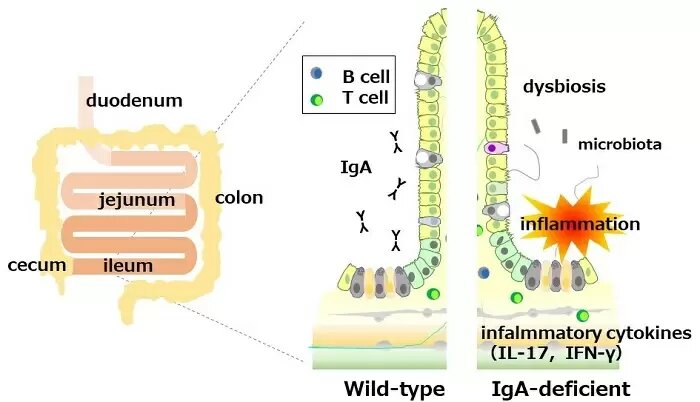
Immunoglobulin A, commonly known as IgA, is an essential antibody that plays a pivotal role in defending our body's mucous membranes. Found in the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital tracts, IgA acts as the first line of defense against invading pathogens. Unlike other antibodies, IgA exists in two distinct forms – serum IgA, circulates in the blood, while secretory IgA (sIgA) is found in mucosal secretions.
Keywords: serum IgA, sIgA, mucosal secretions
Section 2: The Immune Functions of IgA (250 words)
The primary function of IgA is to neutralize pathogens at the site of entry, preventing them from colonizing our mucosal surfaces. It accomplishes this by binding to specific pathogens and toxins, inhibiting their ability to adhere to the epithelial cells within mucous membranes.
Moreover, IgA also plays a vital role in passive immunity, transferring immune protection from the mother to the newborn through breast milk. This ensures that the baby receives essential immunity against common pathogens during the early stages of life.
Keywords: passive immunity, breast milk, pathogens
Section 3: Production and Regulation of IgA (250 words)
IgA production occurs predominantly in the mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), situated in various parts of the body such as the gut, respiratory tract, and mammary glands. Initially, antigen-presenting cells process antigens and present them to B-cells, triggering the production and differentiation of IgA plasma cells.
Regulation of IgA production involves a complex interplay between various factors, including cytokines and gut microbiota. Imbalances in gut microbial populations may influence IgA production, leading to compromised mucosal immunity.
Keywords: mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue, B-cells, gut microbiota, cytokines
Section 4: The Significance of IgA in Disease Prevention (250 words)
IgA deficiency can increase the susceptibility to infections, particularly those affecting the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Deficiencies in IgA production have also been associated with autoimmune disorders and allergic diseases, emphasizing the critical role IgA plays in maintaining overall health.
Understanding IgA dynamics can aid in therapeutic interventions. Research is underway to explore the potential of IgA-based therapies in treating conditions such as gut-related disorders and chronic respiratory infections.
Keywords: IgA deficiency, respiratory infections, autoimmune disorders, therapeutic interventions
Conclusion (100 words):
In conclusion, Immunoglobulin A (IgA) emerges as a superhero antibody, protecting our mucosal surfaces from harmful invaders. Its unique ability to neutralize pathogens at the site of entry and transfer passive immunity makes it an invaluable component of our immune defense system. Understanding the intricate mechanisms involved in IgA production and regulation is crucial in maintaining optimal mucosal health. As research on IgA continues to advance, we can hope for breakthroughs that will revolutionize healthcare and aid in the development of targeted therapies to combat a wide range of diseases.
Keywords: superhero antibody, mucosal health, breakthroughs, targeted therapies
